Substitute Dominants
August 8, 2015
The Guitar Neck
August 8, 2015The Parts of the Guitar
[lollum_dropcap]W[/lollum_dropcap]hen you sit down with other guitarists to talk shop you’re going to want to sound like you know what you’re talking about.
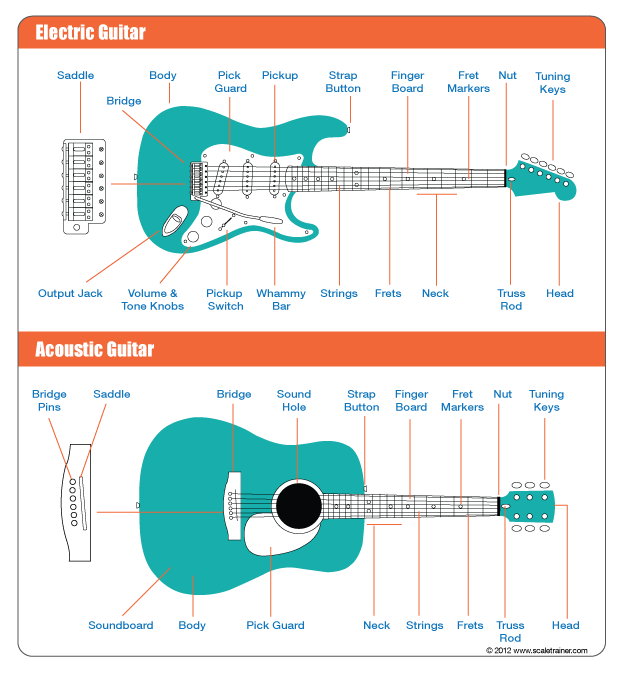
The first thing that you’ll need to make sure you’re familiar with are all the parts of the guitar. Some are commonly know, while others are a bit trickier.
Let’s take a look at them below.
The Parts of the Guitar
- Body: This is the main part of the guitar and will affect the overall sound depending on the wood it is constructed from and whether it’s solid or hollow inside.
- Bridge: The bridge is attached to the body and anchors the strings in place.
- Bridge Pins: On an acoustic guitar these pins secure the strings in the bridge
- Finger Board: The finger board is the layer of wood between the neck and the strings. It also has an effect on the sound of the guitar depending on the type of wood.
- Frets: These are steel bars that run across the fret board. These stop the string at certain lengths changing its pitch.
- Fret Markers: These inlays are like landmarks on the neck letting you know where you are.
- Head: Also referred to as the headstock, it is where the tuning keys are attached.
- Neck: Connecting the body and the head, the neck’s wood choice will also affect the
- sound of the guitar. There are many neck shapes to suit each player’s taste.
- Nut: The nut holds the strings at the end of the fret board, They can be made from plastic, bone, brass, and graphite.
- Output Jack: This is where electric guitars are plugged in. The signal would then travel through a cable and into an amp.
- Pick Guard: The pick guard is part protective layer, part stylistic element.
- Pickup: The pickup can be thought of as a microphone for the strings. It is a magnet wrapped with wire that converts the vibration of the strings into electric current which is sent to the output jack.
- Pickup Switch: If your guitar has more then one pickup this switch will let you choose which pickup(s) you want to use.
- Saddle: The saddle is part of the bridge and keeps the strings free floating above the body.
- Sound Board: On an acoustic guitar the soundboard plays the biggest role in determining the sound and how far it projects. They are most often made of spruce.
- Sound Hole: This is a hole cut into the soundboard to further amplify the sound.
- Strap Button: These buttons are used to attach a strap to the guitar.
- Strings: There are six strings on a standard guitar. Other common models feature 7, 8 , or 12 strings.
- Truss Rod: The truss rod is located inside the neck and runs it’s length. It is used to adjust the curve of the neck forward or backward.
- Tuning Keys: These machines are used to tighten or loosen each string to the desired pitch.
- Volume & Tone Knobs: These knobs are wired between the pickups and the output jack. They control the volume and tonal characteristics of the guitar’s signal.